Creating and managing Cloudera deployments
In this topic, we provide an overview of best practices for deploying Cloudera and demonstrate how to create and manage Cloudera deployments through a simple yet powerful Terraform framework.
If you are looking for a high-level overview of best practices for setting up Cloudera by using our standardized Terraform-based Cloudera deployment patterns, continue reading this article.
What is a Cloudera deployment
A Cloudera deployment is a set of Cloudera management services and data services including related cloud provider resources that exist in your AWS, Azure, or GCP account. It is a combination of the cloud infrastructure that may span multiple cloud providers and regions, and the Cloudera platform that abstracts this underlying cloud provider infrastructure into an integrated, unified, logical data platform layer.
Each Cloudera deployment consists of Cloudera services and the underlying cloud provider resources.
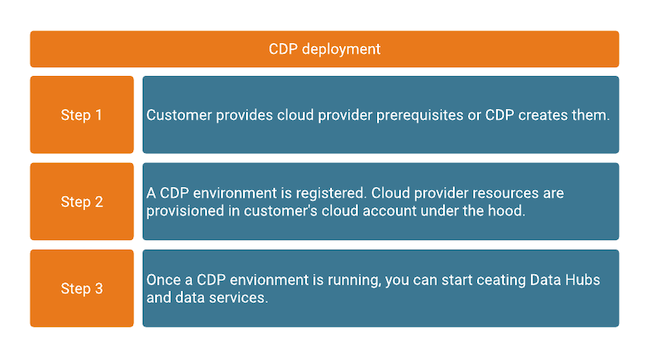
For Cloudera to be deployed, a set of cloud provider prerequisites needs to be provided first, including a virtual network and subnets, storage accounts, and access roles/identities and policies. These cloud provider prerequisites are typically customer-managed and exist in the cloud provider account independently of Cloudera services. As such, they may be shared with other, non-Cloudera cloud services.
Once the cloud provider prerequisites are present, a Cloudera environment can be deployed in the virtual network. Once your Cloudera environment is up and running, your core Cloudera and cloud provider infrastructure is in place and you can start creating Cloudera Data Hub clusters and data services in order to run workloads. When these services are created, additional cloud provider resources such as VM instances, security groups, and load balancers are deployed in your cloud account. For each service, you can select which subnets of the underlying virtual network and what storage locations within your specified storage accounts they should use.
These three high-level deployment steps are described in the following diagram:
Cloudera deployment can be performed by using either Cloudera web interface or Cloudera CLI, or Terraform-based Cloudera deployment patterns. Continue reading to learn about deploying Cloudera using Terraform.
Cloudera deployment patterns
To simplify the task of defining and creating Cloudera deployments, we provide and describe a set of predefined target architectures recommended by Cloudera. These target architectures are called deployment patterns.
In Cloudera’s Terraform framework, each pattern is represented by a deployment template that allows you to quickly instantiate one of the reference deployments. The templates can be used as a starting point and modified according to your needs. You can learn more about the recommended configurations of Cloudera on cloud from the documentation of our end-to-end deployment patterns as well as our network reference architectures for AWS and Azure.
Currently, we provide templates that represent the following deployment patterns, each matching a different use case:
| Private | Production-like setup fully deployed on private subnets without public IPs or direct outbound internet access. Demonstrates a possible production deployment with typical network security features enabled. |
| Semi-private | Production-like setup with access over the public internet to the user interfaces and API endpoints only. It serves as a reference for production deployments without the need for configuring VPNs, jump hosts, and user-defined routing for outbound (egress) traffic |
| Public | Simple setup with access over public internet to all endpoints and with a minimal footprint. It can be used for quick testing, tutorial, demonstration, or simply to understand the internal workings of Cloudera on cloud. This setup is not secure enough for production but can be used for proof of concept. |
Cloudera deployment pattern definitions
Deployment patterns are predefined architectures recommended by Cloudera that simplify the task of defining and creating Cloudera deployments. There are many options available for deploying Cloudera, but as a best practice, Cloudera recommends that you use one of the following three deployment patterns: private, semi-private, or public.
These patterns are based on the identically named network reference architectures and extend them, by incorporating Cloudera’s recommended configuration for deploying Cloudera in multiple availability zones, selecting the Data Lake scale, configuring storage access policies, and setting up fine-grained access control.
As can be expected, each of these deployment patterns brings a unique trade-off among various aspects, such as ease of setup, security provided, workloads supported, and so on. Read the following content to understand what specific networking, IAM, and storage cloud provider configurations, and Cloudera configurations are applied as part of the supported deployment patterns.
