Configuring Extraction for Altus Clusters on AWS
- Any HDFS paths in a job, query, or data entity are extracted as proxy entities for the path, similar to how Hive entities are extracted. That means that HDFS is not bulk extracted from an Altus cluster.
- Hive Metastore (HMS) entities are also not bulk extracted. Cloudera Navigator extracts Hive entities used in queries that generate lineage, such as databases, tables, and so on.
Requirements
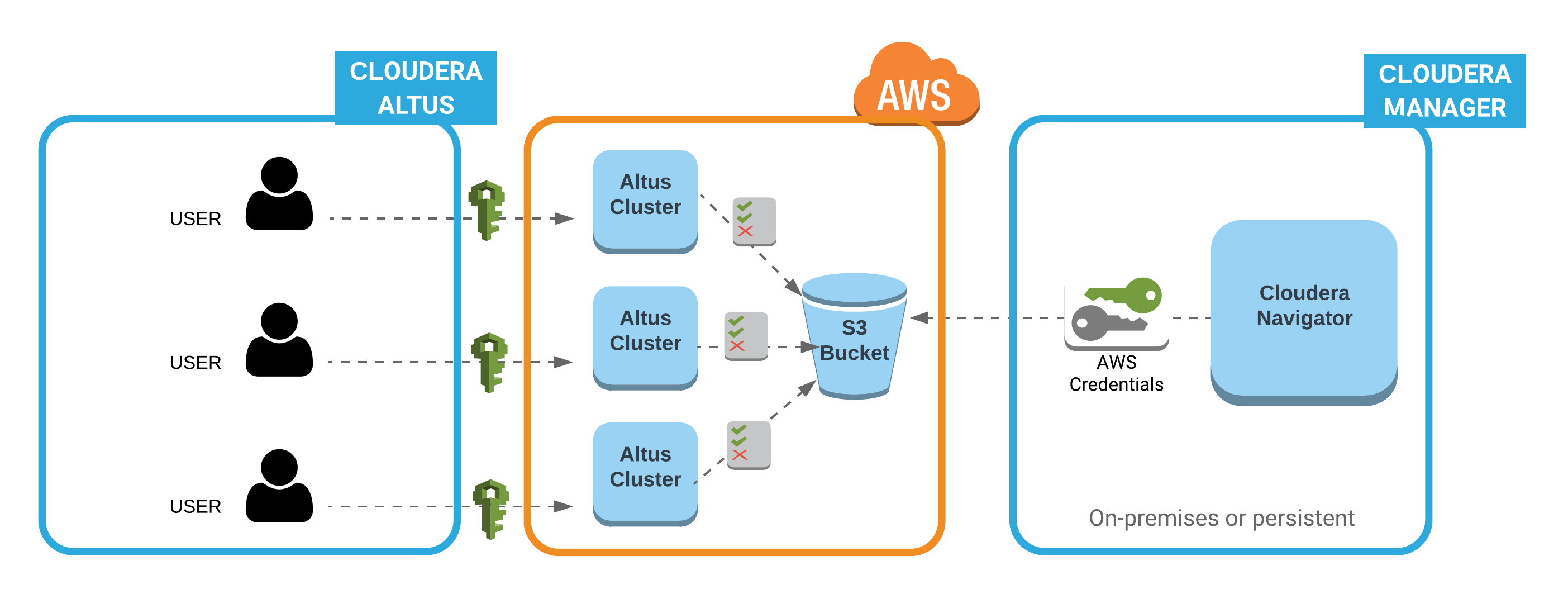
Cloudera Navigator collects metadata and lineage entities from transient clusters deployed to AWS by Cloudera Altus users. The metadata and lineage data is not collected directly from the transient clusters but rather from an Amazon S3 bucket that serves as the storage mechanism for the Telemetry Publisher running in the cluster (see How it Works: Background to the Setup Tasks for details).
- Identifying the Amazon S3 bucket, and
- Configuring correct access permissions to it from both Cloudera Altus and Cloudera Navigator. Transient clusters instantiated by Altus users must have read and write permissions to the Amazon S3 bucket used by Telemetry Publisher. The on-premises centralized Cloudera Navigator instance must have read permissions on the same Amazon S3 bucket.
 —Altus user account (with cross-account privileges to AWS
account). Privileges to launch EC2 clusters and use other AWS resources, including Amazon S3 buckets identified in the Environment (data input, data output, logs, and the bucket for Telemetry
Publisher).
—Altus user account (with cross-account privileges to AWS
account). Privileges to launch EC2 clusters and use other AWS resources, including Amazon S3 buckets identified in the Environment (data input, data output, logs, and the bucket for Telemetry
Publisher).
 — Read and write privileges to the Amazon S3 bucket configured in the
Environment for the Altus user.
— Read and write privileges to the Amazon S3 bucket configured in the
Environment for the Altus user.
 -- AWS access key ID and AWS secret key for the AWS account associated with the Amazon S3
bucket.
-- AWS access key ID and AWS secret key for the AWS account associated with the Amazon S3
bucket.
- An Amazon Web Services account.
- A Cloudera Altus account.
- A Cloudera Altus user account that can run jobs on transient clusters deployed to AWS.
- Access to the on-premises or persistent Cloudera Manager cluster running Cloudera Navigator. The Cloudera Manager user role of Full Administrator and the ability to log in to the Cloudera Manager Admin Console is required.
- AWS Credentials for the AWS account hosting the Amazon S3 bucket that serves as the storage mechanism for metadata and lineage data from clusters on AWS launched by Cloudera Altus.
Obtaining AWS Credentials for the Amazon S3 Bucket
AWS Credentials are available to be downloaded whenever you create an IAM user account through the AWS Management Console. If you are configuring an existing Amazon S3 bucket and you do not have the AWS Credentials for it, you can generate new AWS Credentials from the AWS account using either the AWS Management Console or the AWS CLI.
Generating new AWS Credentials deactivates any previously issued credentials and makes the newly generated credentials Active for the AWS account. Keep that in mind if you obtain new AWS Credentials to use for the Cloudera Navigator-Cloudera Altus integration.
These steps assume you have an AWS account and that an Amazon S3 bucket exists on that account that you want to use as the storage location for metadata and lineage.
- Log in to the AWS Management Console using the account associated with the Amazon S3 bucket.
- Navigate to the Security credentials section of the Users page in IAM for this account. For example:
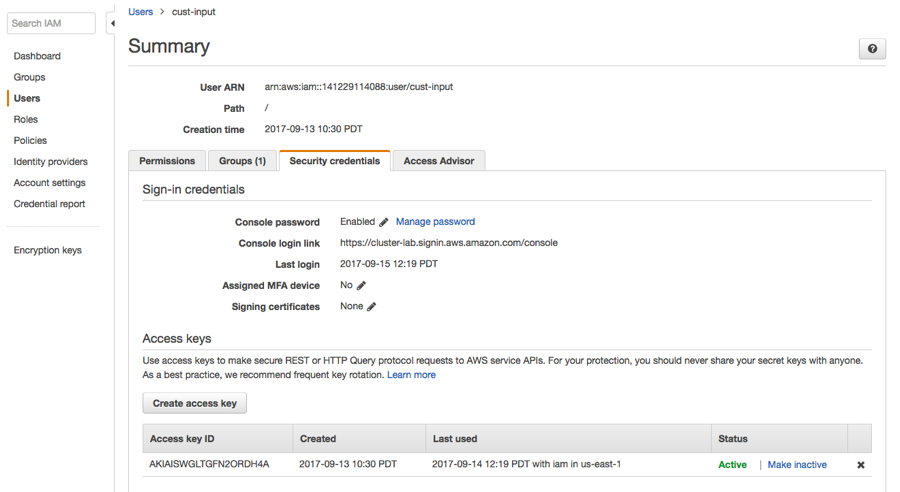
- Click the Create access key button to generate new AWS Credentials. Extract the credentials (the Access Key Id and Secret Key) from the user interface or download the credentials.csv for later use.
New credentials can be created by using the AWS CLI rather than the AWS Management Console. See Amazon documentation for details.
Cloudera Altus Configuration
Cloudera Altus instantiates single-user transient clusters focused on data engineering workloads that use compute services such as Hive, Impala, or MapReduce2. The typical deployment scenario involves running scripts that invoke the Cloudera Altus CLI to instantiate the cluster, in this case, using Amazon Web Services according to the details specified in the Altus Environment. An Altus environment specifies all resources needed by the cluster, including the AWS account that will be used to instantiate the cluster. The Cloudera Altus user account is configured to provide cross-account access to the AWS account that has permissions to launch AWS Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances and use other AWS resources, including Amazon S3 buckets.
Although the Altus Environment can be created using Quickstart, Cloudera recommends using the Environment Wizard or the Altus CLI instead. The Wizard provides better control over configuring resources, including letting you specify the Amazon S3 bucket that clusters will use to store metadata and lineage information for collection by Cloudera Navigator. Specifically, the Resources & Policies page of the Configuration Wizard lets you enable integration with Cloudera Navigator and specify the Amazon S3 bucket that will hold collected metadata and lineage information.
- Click the Enable Cloudera Navigator checkbox to enable the feature.
- In the Cloudera Navigator S3 Data Bucket field, enter the path to the Amazon S3 bucket, including the final /, which
identifies the target as an S3 bucket. For example:
s3a://cluster-lab.example.com/cust-input/
Cloudera Navigator Configuration
- Follow the steps in Adding AWS Credentials and Configuring Connectivity to add new or regenerated AWS Credentials to the Cloudera Manager Server and then configure connectivity.
- Follow the steps in Configuring Connectivity for AWS Credentials to configure connectivity for AWS Credentials that are already available to be used for the Amazon S3 bucket but have not yet been configured for connectivity.
Adding AWS Credentials and Configuring Connectivity
Cloudera Manager Required Role: Full Administrator
- Log in to the Cloudera Manager Admin Console.
- Select Administration > AWS Credentials.
- Click the Add Access Key Credentials button on the AWS Credentials page.
- Enter a meaningful name for the AWS Credential, such as the type of jobs the associated clusters will run (for example, etl-processing). This name is for your own information and is not checked against any Cloudera Altus or AWS attributes.
- Enter the AWS Access Key ID and the AWS Secret Key.
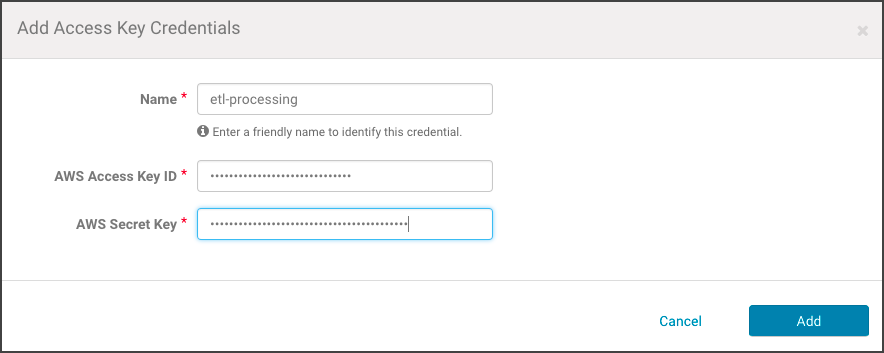
- Click Add to save the credentials. The S3Guard option page displays, reflecting the credential name (for example, Edit S3Guard: etl-processing). Disregard this option.
- Click Save. The Connect to Amazon Web Services page displays, showing the options available for this specific AWS credential.
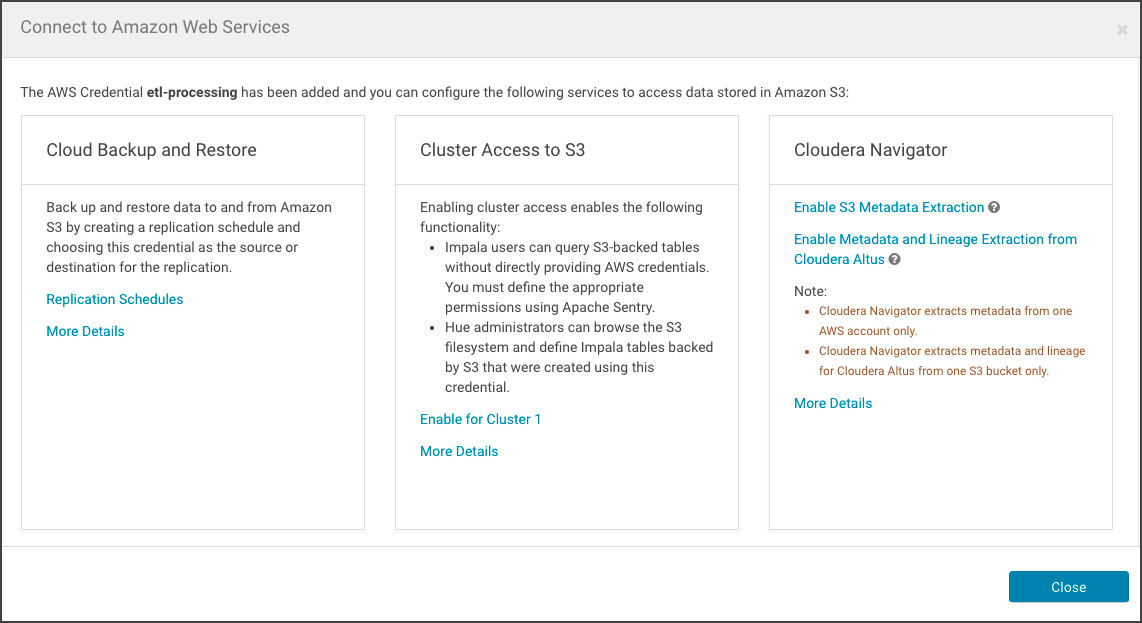
- Click Enable Metadata and Lineage Extraction from Cloudera Altus. The Metadata and Lineage Extraction Configuration setting page displays a field for specifying the Amazon S3 bucket name.
- Enter the name of the Amazon S3 bucket. For example:
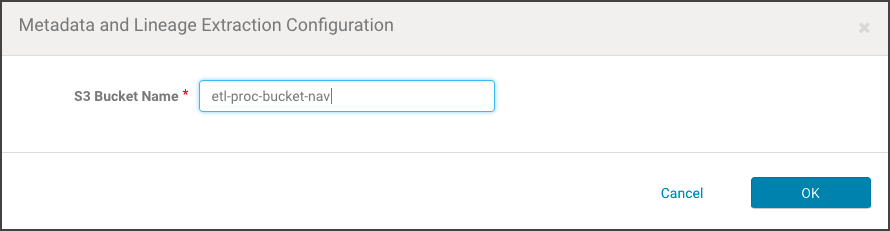
- Click OK. The AWS Credentials page re-displays, and the newly added AWS Credential is listed with any other AWS Credentials held by the Cloudera Manager Server.
- Restart the Cloudera Management Service.
Configuring Connectivity for AWS Credentials
- Log in to the Cloudera Manager Admin Console.
- Select Administration > AWS Credentials.
- Find the available AWS Credentials that provide access to the Amazon S3 bucket used to collect metadata and lineage from transient clusters.
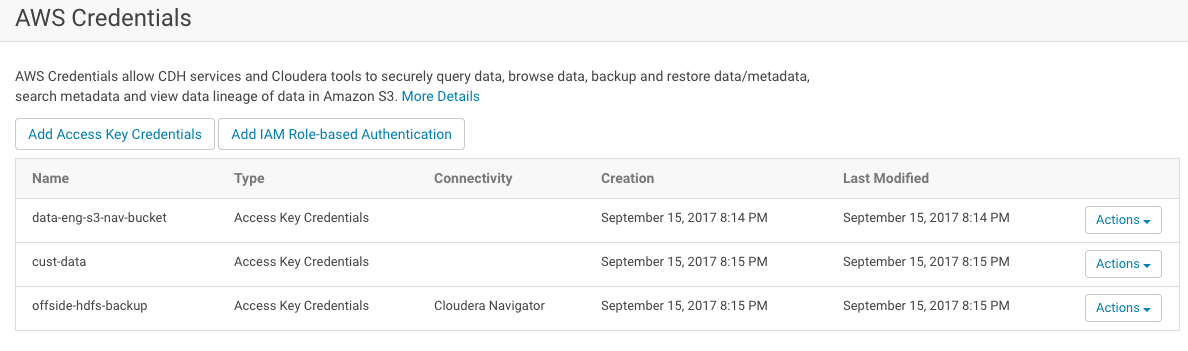
- Click the Actions drop-down menu and select Edit Connectivity. The Connect to Amazon Web Services page displays the three sections of possible configurations.
- In the Cloudera Navigator section, click the Enable Metadata and Lineage Extraction from Cloudera Altus link. The Metadata and Lineage Extraction Configuration page displays.
- Enter the name of the Amazon S3 bucket in the S3 Bucket Name field.
- Click OK.
- Restart the Cloudera Management Service.
This completes the setup process. After the restart, metadata and lineage for transient clusters deployed using Cloudera Altus should be available in the Cloudera Navigator console.
- Cluster (Source Type)
- Cluster-name (Cluster Group)
- Transient (Deployment Type)
- Cluster Template, Cluster Instance (Classname)
See Search: Syntax and Properties Reference for more information.
Categories: AWS | Altus | Cloud | Data Management | Navigator | All Categories