Using Cloudera Navigator with Amazon S3
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is a storage solution offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that provides highly available storage in the cloud. Clusters deployed not only in the AWS cloud but also on-premises are using Amazon S3 as persistent storage. Common use cases include BDR (backup and disaster recovery) and persistent storage for transient clusters deployed to the cloud, such as storage for ETL workload input and output.
This section provides conceptual information about Amazon S3 storage and shows you how to configure Cloudera Navigator to extract metadata and lineage from an Amazon S3 bucket.
Amazon S3 Storage Characteristics
Amazon S3 is an object store rather than a file store or block store. It does not have the hierarchy found in typical filesystems. Amazon S3 uses the construct of a bucket as a container for objects. An object can be any kind of file—text file, image, photo, graphic, video, an ETL bundle to be ingested into a cluster, and so on.
Files can be added to Amazon S3 through the AWS Management Console, by using the AWS CLI, or by using scripts that invoke the CLI.
Amazon S3 storage is highly available because Amazon replicates data across multiple servers within its data centers and uses an eventual consistency model—not all accesses of an object on Amazon S3 may be reflected concurrently or instantaneously. However, eventually, all updates to data across servers are synchronized. The eventual consistency model can result in a short delay between the time objects are uploaded to Amazon S3 and the time their metadata is available in Cloudera Navigator. This is expected behavior and simply how eventual consistency works.
For more information about Amazon S3, see Amazon S3 documentation.
Cloudera Navigator and Amazon S3
Despite the implementation details of Amazon S3 storage, Cloudera Navigator collects metadata for Amazon S3 entities in much the same way as for HDFS entities, with some exceptions shown in the table below.
| Feature | Amazon S3 | Cloudera Navigator |
|---|---|---|
| User-defined metadata consists of custom key-value pairs (in which each key is prefixed with x-amz-meta-) that can be used to tag objects on Amazon S3. |  |
 |
| System-defined metadata includes properties such as Date, Content-Length, Last-Modified. Some system-defined properties comprise the Technical Metadata for the object in Cloudera Navigator. |  |
 |
| Tags for buckets and objects |  |
 |
| Versioning is not supported. Cloudera Navigator extracts metadata and lineage from the latest version only. |  |
 |
| Unnamed directories |  |
 |
| Object lifecyle rules. See Object Lifecycle Rules Constraints for more information. |  |
 |
| Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS). See Amazon SQS and Amazon SNS Constraints for usage limitations and requirements. |  |
 |
| Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS). See Amazon SQS and Amazon SNS Constraints for usage limitations and requirements. |  |
 |
Object Lifecycle Rules Constraints
Cloudera Navigator does not support lifecycle rules that remove objects from Amazon S3. For example, an object lifecycle rule that removes objects older than n days deletes the object from Amazon S3 but the event is not tracked by Cloudera Navigator. This limitation applies to removing objects only. Using lifecycle rules requires using bulk-only extraction. See Custom Configurations for details about configuring the necessary AWS Policy and applying it to the Amazon S3 bucket for use by Cloudera Navigator.
Amazon SQS and Amazon SNS Constraints
Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) is a distributed, highly scalable hosted queue for storing messages. Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) is publish-subscribe notification service that coordinates message delivery. Both services can be configured for use with Amazon S3 storage buckets. For example, Amazon S3 storage buckets can send notification messages to one or more queues or to email addresses whenever specified events occur, such as creating, renaming, updating, or deleting data on the Amazon S3 bucket.
During the default configuration process, Cloudera Navigator transparently sets up an Amazon SQS queue and configures Amazon S3 event notification for each bucket. The queue is used to hold event messages that are subsequently collected by the Cloudera Navigator S3 extractor process, for incremental extracts. Use the default configuration process only for Amazon S3 buckets that do not have existing queues or notifications configured.
For Amazon S3 buckets that are already configured for queues, use the custom configuration process—sometimes referred to as "Bring Your Own Queue" (BYOQ)—to manually configure queues for Cloudera Navigator. For Amazon S3 buckets that are already configured for notifications, use the BYOQ custom configuration in conjunction with Amazon SNS in a fan-out configuration. In a fan-out scenario, an Amazon SNS message is sent to a topic and then replicated and pushed to multiple Amazon SQS queues, HTTP endpoints, or email addresses. See Common Amazon SNS Scenarios for more information about fan-out configuration, and see Custom Configurations for details about configuring Cloudera Navigator when the Amazon S3 bucket is already set up for either Amazon SQS or Amazon SNS.
Object Storage and Implicit Folder Limitation
Amazon S3 storage does not use a directory structure or other hierarchy as found in a traditional file system. Each object has an object key name that identifies the object by its S3Uri location—the path to the object. This path includes the object, prefix if any, and bucket name. Including the S3 protocol specifier, the pattern is as follows:
s3://bucketname/prefix/objectkey
There can be more than one prefix in an object key name. Prefixes are separated by the forward slash character (/). Although Amazon S3 provides a folder metaphor for organizing objects in an S3 bucket, the folder does not provide actual containment or structure: it is the object key name and its S3Uri location that identifies the object.
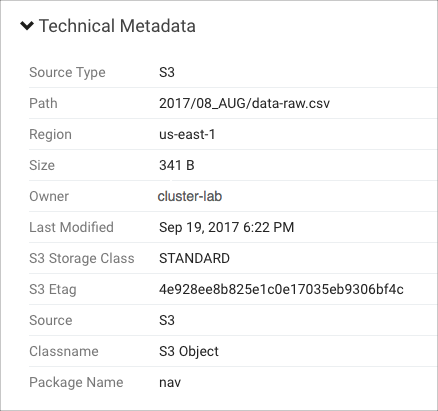
Cloudera Navigator mimics file system behavior by mapping elements of the object key name to implicit folders. For example, for an Amazon S3 file with the object key name 2017/08_AUG/data-raw.csv, Cloudera Navigator creates an entity with the path 2017/08_AUG/data-raw.csv and also creates two directories: 2017 and 2017/08_AUG.
| Cloudera Navigator | Amazon S3 |
|---|---|
 |
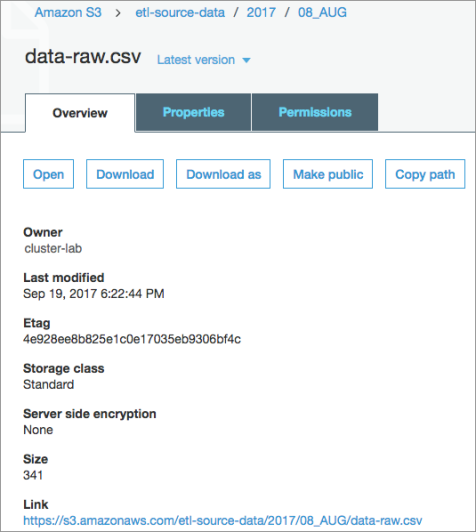 |
Cloudera Navigator console Lineage tab for the file with object key 2017/08_AUG/data-raw.csv shows it in the context of implicit folders:

Cloudera Navigator has some limitations specifically for deleted objects and implicit folders as follows:
- Cloudera Navigator does not mark an implicit folder as deleted even after all its child objects have been deleted.
- Cloudera Navigator does not mark as deleted any objects and folders deleted using Amazon S3 tools, such as the AWS CLI (aws s3 commands) or the AWS Management Console.
For more details about the properties shown by Cloudera Navigator, see S3 Properties.
Despite the differences between an object store and a hierarchical store, data engineers can work with Amazon S3 using the Cloudera Navigator in much the same way as for HDFS and other entities.
Overview of Amazon S3 Extraction Processes
By default, Cloudera Navigator uses combined bulk and incremental extraction processes. An initial bulk process extracts all metadata from an Amazon S3 bucket during the configuration process. Subsequent extracts are incremental. Changes are collected from an Amazon SQS queue created by Cloudera Navigator during the default configuration process.
- For the bulk extract, Cloudera Navigator invokes the Amazon S3 API.
- For the incremental extract, Cloudera Navigator invokes the Amazon SQS API.
Amazon meters usage and charges differently for each of these APIs.
API Usage and Setting Limits
- If the limit is set is reached in any given 30-day interval, Cloudera Navigator suspends extraction from the configured Amazon S3 buckets until the next 30-day interval begins.
- When the new 30-day interval begins, Cloudera Navigator extracts any data that was not extracted while extraction was suspended.
- Use Cloudera Manager Admin Console to access the Navigator Metadata Server Advanced Configuration Snippet (Safety Valve) for cloudera-navigator.properties.
- Set the value of any_int to your chosen limit.
nav.aws.api.limit=any_int
Categories: Data Management | Governance | Metadata | Navigator | S3 | All Categories