Auditing and Data Lineage
Organizations of all kinds want to understand where data in their clusters is coming from and how it is used. Cloudera Navigator Data Management component is a fully integrated data management and security tool for the Hadoop platform that has been designed to meet compliance, data governance, and auditing needs of global enterprises. Without Cloudera Navigator, Hadoop clusters rely primarily on log files for auditing. However, log files are not an enterprise-class real-time auditing or monitoring solution. For example, log files can be corrupted by a system crash during a write commit.
Cloudera Navigator Data Management
Cloudera Navigator captures a complete and immutable record of all system activity. An audit trail can be used to determine the particulars—the who, what, where, and when—of a data breach or attempted breach. Auditing can be used to not only identify a rogue administrator who deleted user data, for example, but can also be used to recover data from a backup. Enterprises that must prove they are in compliance with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), PCI (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard), or other regulations associated with sensitive or personally identifiable data (PII) are required to produce auditing records when asked by government or other officials, such as banking regulators.
Auditing also serves to provide a historical record of data and context for data forensics. Data stewards and curators can use auditing reports to determine consumption and use patterns across various data sets by different user communities, for optimizing data access.
This section provides a brief overview of functionality of Cloudera Navigator. For complete details, see Cloudera Navigator Data Management.
Continue reading:
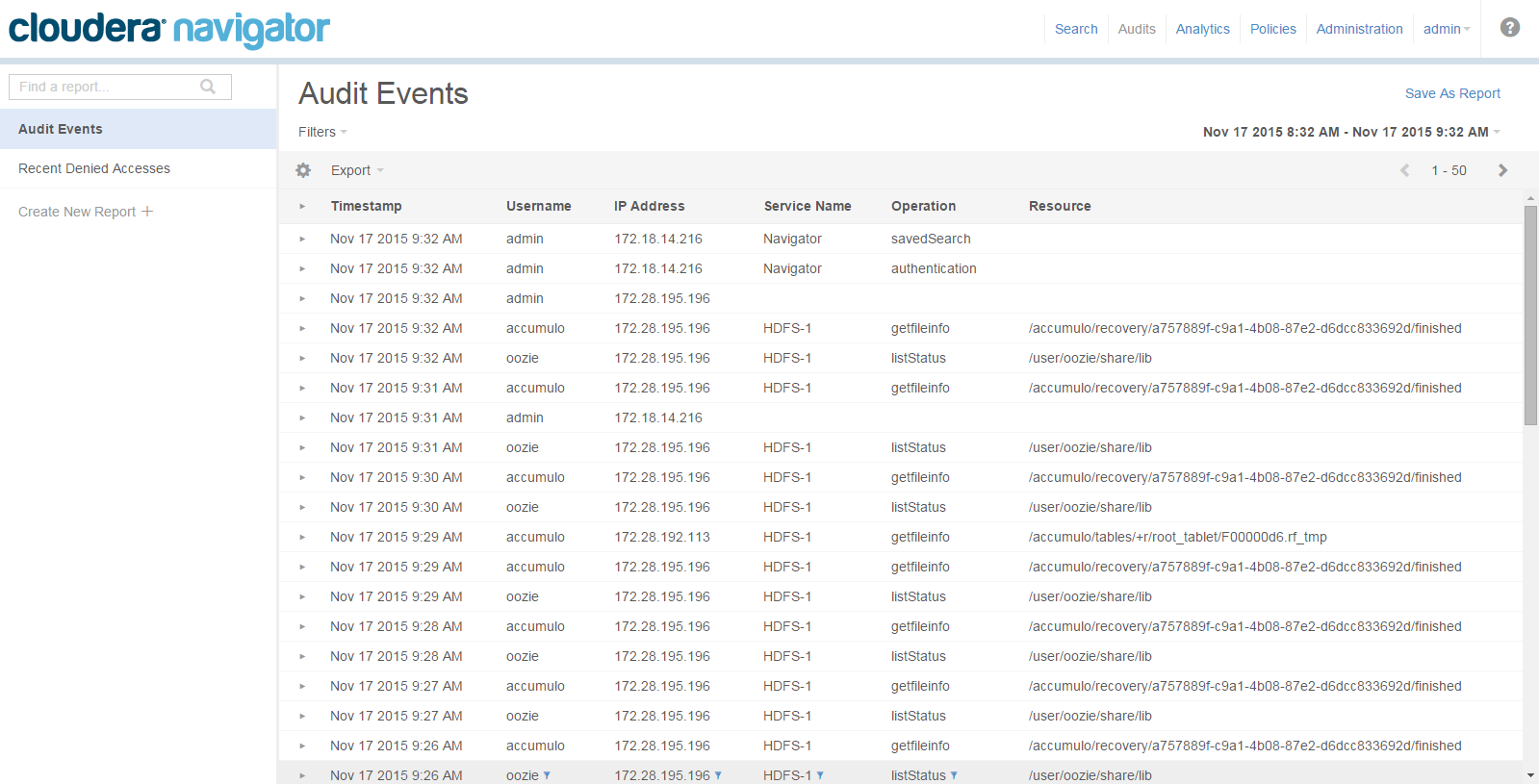
Auditing
While Hadoop has historically lacked centralized cross-component audit capabilities, products such as Cloudera Navigator add secured, real-time audit components to key data and access frameworks. Using Cloudera Navigator, administrators can configure, collect, and view audit events, to understand who accessed what data and how.
- HDFS entities accessed by HDFS, Hive, HBase, Impala, and Solr services
- HBase and Impala
- Hive metadata
- Sentry
- Solr
- Cloudera Navigator Metadata Server
Metadata Management
Cloudera Navigator features complete metadata storage and supports data discovery. It consolidates technical metadata for all cluster data and enables automatic tagging of data based on the external sources entering the cluster. The consolidated metadata store is searchable through the Cloudera Navigator console, a web-based unified interface.
In addition, Cloudera Navigator supports user-defined metadata that can be applied to files, tables, and individual columns, to identify data assets for business context. The result is that data stewards can devise appropriate classification schemes for specific business purposes and data is more easily discovered and located by users.
Furthermore, policies can be used to automatically classify and applying metadata to cluster data based on arrival, scheduled interval, or other trigger.
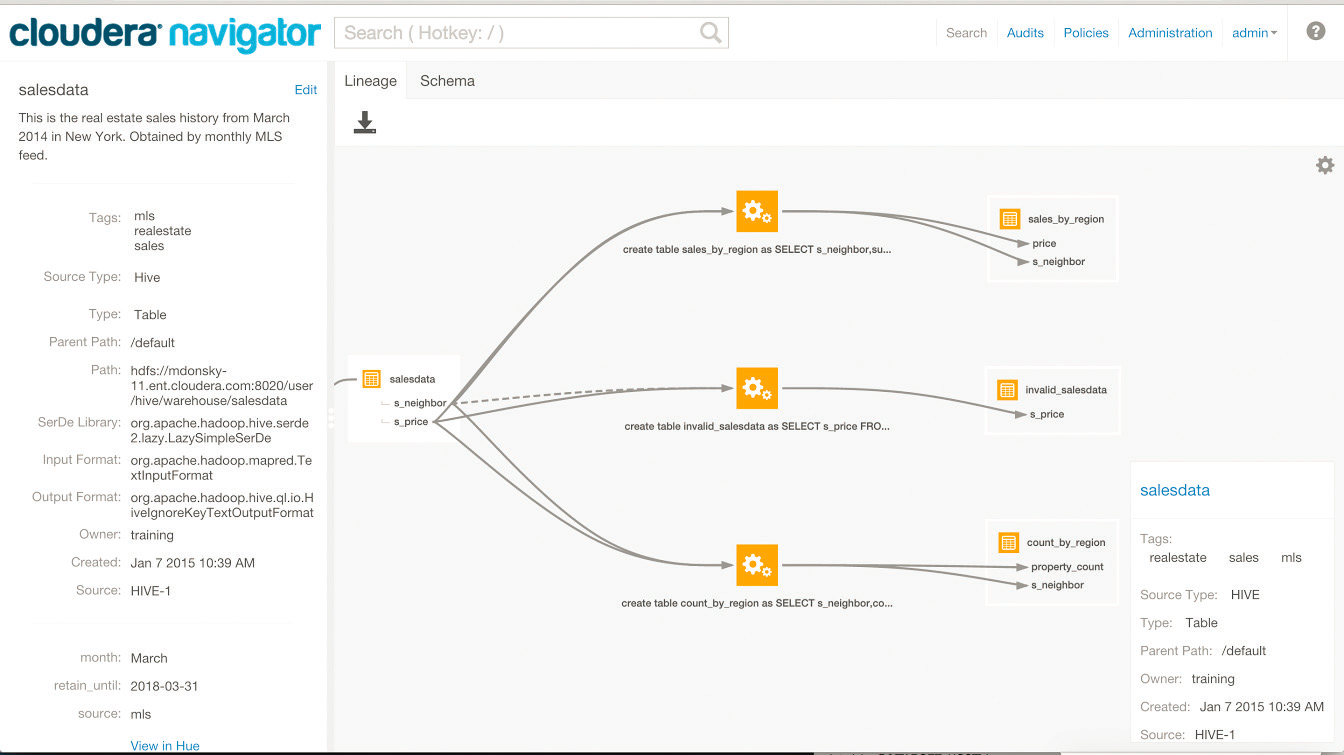
Lineage
Cloudera Navigator lineage is a visualization tool for tracing data and its transformations from upstream to downstream through the cluster. Lineage can show the transforms that produced upstream data sources and the effect the data has on downstream artifacts, to the column level. Cloudera Navigator tracks lineage of HDFS files, datasets, and directories, Hive tables and columns, MapReduce and YARN jobs, Hive queries, Impala queries, Pig scripts, Oozie workflows, Spark jobs, and Sqoop jobs.
Integration within the Enterprise
- Using syslog as a mediator between raw-event stream generated by Hadoop cluster and the SIEM tools.
- Using a REST API for custom enterprise tools.
- Exporting data to CSV or other text file.
Auditing and Components
The table below details auditing capabilities of Cloudera Manager and CDH components.
| Component | Auditing Capabilities |
|---|---|
| HDFS | Events captured by Cloudera Navigator (including security events) |
| MapReduce | Inferred through HDFS |
| YARN | Inferred through HDFS |
| Accumulo | Log Files - Partial inclusion of security events; does not include non-bulk writes |
| Flume | Log Files |
| HBase | Audit events captured by Cloudera Navigator (including security events) |
| HiveServer2 | Audit events captured by Cloudera Navigator |
| Hue | Inferred through underlying components |
| Impala | Audit events captured by Cloudera Navigator |
| Kafka | Log Files |
| Oozie | Log Files |
| Pig | Inferred through HDFS |
| Search | Log Files |
| Sentry | Audit events captured by Cloudera Navigator |
| Spark | Inferred through HDFS |
| Sqoop | Log Files |
| Sqoop2 | Log Files (including security events) |
| ZooKeeper | Log Files |
| Cloudera Manager | Audit events captured by Cloudera Navigator (partial capture of security events) |
| Cloudera Navigator | Audit events captured by Cloudera Navigator itself |
| Backup and Disaster Recovery | None |
Security Events
- User data read
- User data written
- Permission changes
- Configuration changes
- Login attempts
- Escalation of privileges
- Session Tracking
- Key Operations (Key Trustee)