Cloudera Search Architecture
Cloudera Search runs as a distributed service on a set of servers, and each server is responsible for a portion of the searchable data. The data is split into smaller pieces, copies are made of these pieces, and the pieces are distributed among the servers. This provides two main advantages:
- Dividing the content into smaller pieces distributes the task of indexing the content among the servers.
- Duplicating the pieces of the whole allows queries to be scaled more effectively and enables the system to provide higher levels of availability.
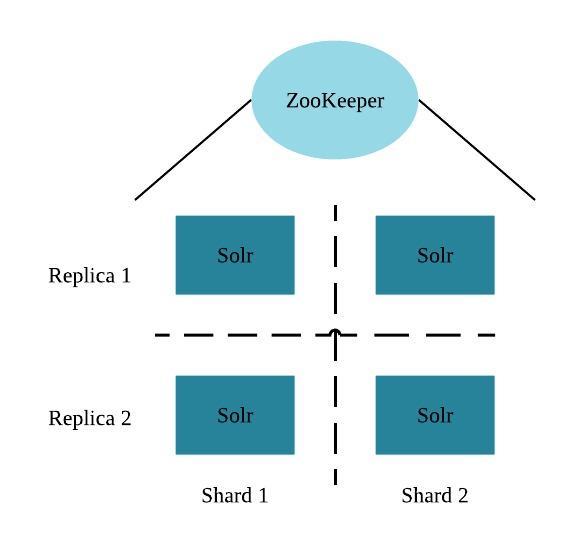
Each Cloudera Search server can handle requests independently. Clients can send requests to index documents or perform searches to any Search server, and that server routes the request to the correct server.
Each Search deployment requires:
- ZooKeeper on at least one host. You can install ZooKeeper, Search, and HDFS on the same host.
- HDFS on at least one, but as many as all hosts. HDFS is commonly installed on all cluster hosts.
- Solr on at least one but as many as all hosts. Solr is commonly installed on all cluster hosts.
More hosts with Solr and HDFS provides the following benefits:
- More Search servers processing requests.
- More Search and HDFS collocation increasing the degree of data locality. More local data provides faster performance and reduces network traffic.
The following graphic illustrates some of the key elements in a typical deployment.
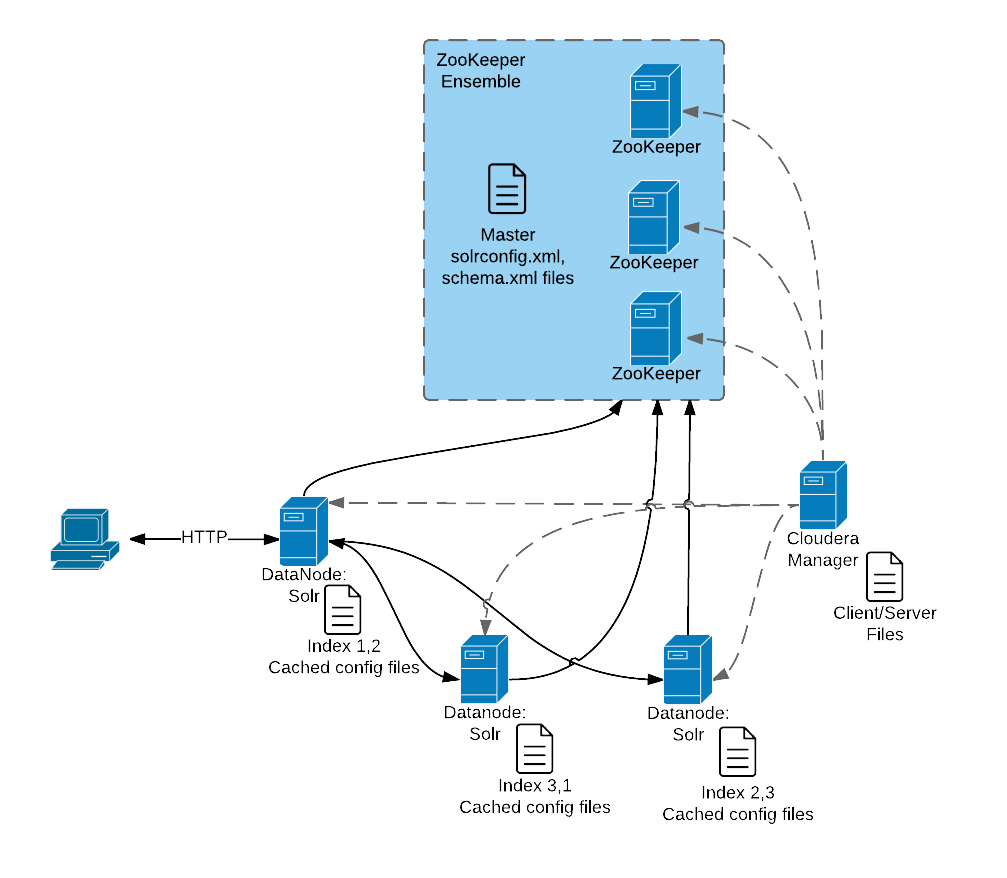
This graphic illustrates:
- A client submits a query over HTTP.
- The response is received by the NameNode and then passed to a DataNode.
- The DataNode distributes the request among other hosts with relevant shards.
- The results of the query are gathered and returned to the client.
Also notice that the:
- Cloudera Manager provides client and server configuration files to other servers in the deployment.
- ZooKeeper server provides information about the state of the cluster and the other hosts running Solr.
The information a client must send to complete jobs varies:
- For queries, a client must have the hostname of the Solr server and the port to use.
- For actions related to collections, such as adding or deleting collections, the name of the collection is required as well.
- Indexing jobs, such as MapReduceIndexer jobs, use a MapReduce driver that starts a MapReduce job. These jobs can also process morphlines and index the results to Solr.
Cloudera Search Configuration Files
Configuration files in a Cloudera Search deployment include:
- Solr config files stored in ZooKeeper:
- solrconfig.xml: Contains Solr configuration parameters.
- schema.xml: Contains configuration that specifies the fields a document can contain, and how those fields are processed when adding documents to the index, or when querying those fields.
- Files copied from hadoop-conf in HDFS configurations to Solr servers:
- core-site.xml
- hdfs-site.xml
- ssl-client.xml
- hadoop-env.sh
- topology.map
- topology.py
- Cloudera Manager manages the following configuration files:
- cloudera-monitor.properties
- cloudera-stack-monitor.properties
- Logging and security configuration files:
- log4j.properties
- jaas.conf
- solr.keytab
- sentry-site.xml
You can use parcels or packages to deploy Search. Some files are always installed to the same location and some files are installed to different locations based on whether the installation is completed using parcels or packages.
Client Files
Client files are always installed to the same location and are required on any host where corresponding services are installed. In a Cloudera Manager environment, Cloudera Manager manages settings. In an unmanaged deployment, all files can be manually edited. Client configuration locations are:- /etc/solr/conf for Solr client settings files
- /etc/hadoop/conf for HDFS, MapReduce, and YARN client settings files
- /etc/zookeeper/conf for ZooKeeper configuration files